CV-CLOTEZ (Eq. pGEM-T-Easy)
CV-CLOTEZ (Eq. pGEM-T-Easy)
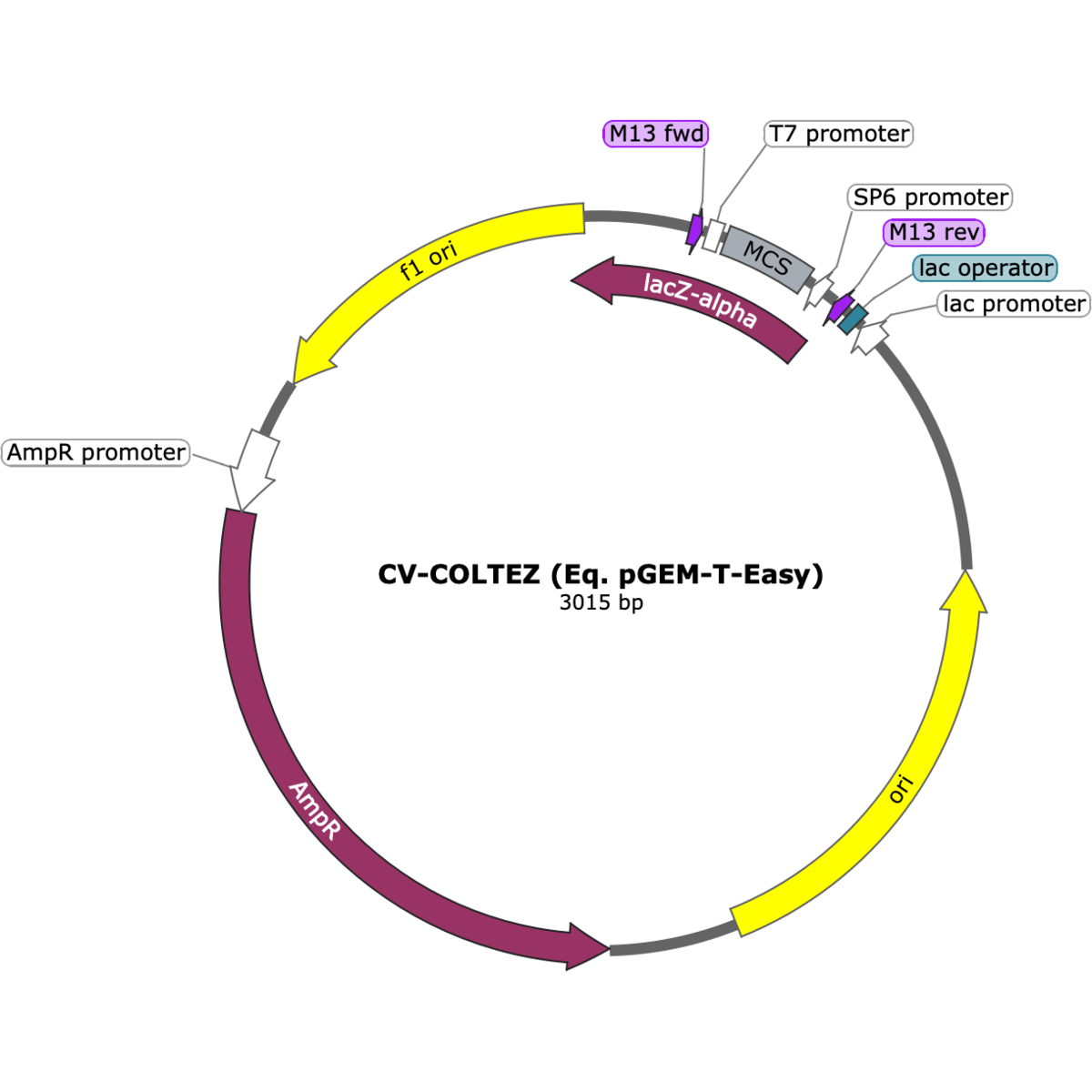
CV-CLOTEZ has a sequence identical to the pGEM-T Easy vector. This high-copy plasmid carries an ampicillin resistance marker and a ColE1-derived origin, and is designed for TA cloning of PCR products generated by Taq polymerase. It includes a multiple cloning site within the lacZα fragment, allowing blue–white screening of recombinants in E. coli.
Format: 2 tubes with 5 µg in 5 µl of TE
Couldn't load pickup availability
Key Properties
Applications: Cloning
Copy number: High-copy number
Host: E. coli
Selection markers: Amp / Carb (E. coli)
Sequence: CV-COLTEZ_Eq._pGEM-T-Easy.gb
Share
Background
pGEM-T Easy was introduced by Promega as part of the pGEM® system for rapid cloning of PCR products. It is optimized for TA cloning: PCR fragments generated by Taq polymerase, which carry single 3′ A overhangs, efficiently ligate into the vector’s single 3′ T overhangs. CV-CLOTEZ preserves the exact sequence of pGEM-T Easy, ensuring compatibility with published protocols and vendor kits. Original documentation is available in the Promega pGEM®-T and pGEM®-T Easy Vector Systems Technical Manual (PDF).
Features
- Antibiotic selection: Ampicillin (bla)
- Origin of replication: ColE1-derived, high copy (~500–700/cell)
- Size: ~3.0 kb
- Cloning system: Single 3′ T overhangs for direct TA cloning
- MCS: Multiple cloning site within the lacZα fragment for blue–white screening
- Convenience: Compatible with standard ligation reactions using PCR products
Applications
- Rapid cloning of PCR products amplified with Taq DNA polymerase
- Blue–white screening of recombinant clones in E. coli
- High-yield plasmid prep of cloned inserts for downstream applications
- Teaching TA cloning methods in molecular biology courses
- Template for subcloning PCR products into expression vectors
Limitations
- Optimized specifically for Taq polymerase products; proofreading polymerases that generate blunt ends require modification
- Single selection marker (ampicillin) limits dual-plasmid experiments
- High copy number may impose metabolic burden on host cells
- Not designed for direct expression without additional elements
