CV-COL33 (Eq. pBAD33)
CV-COL33 (Eq. pBAD33)
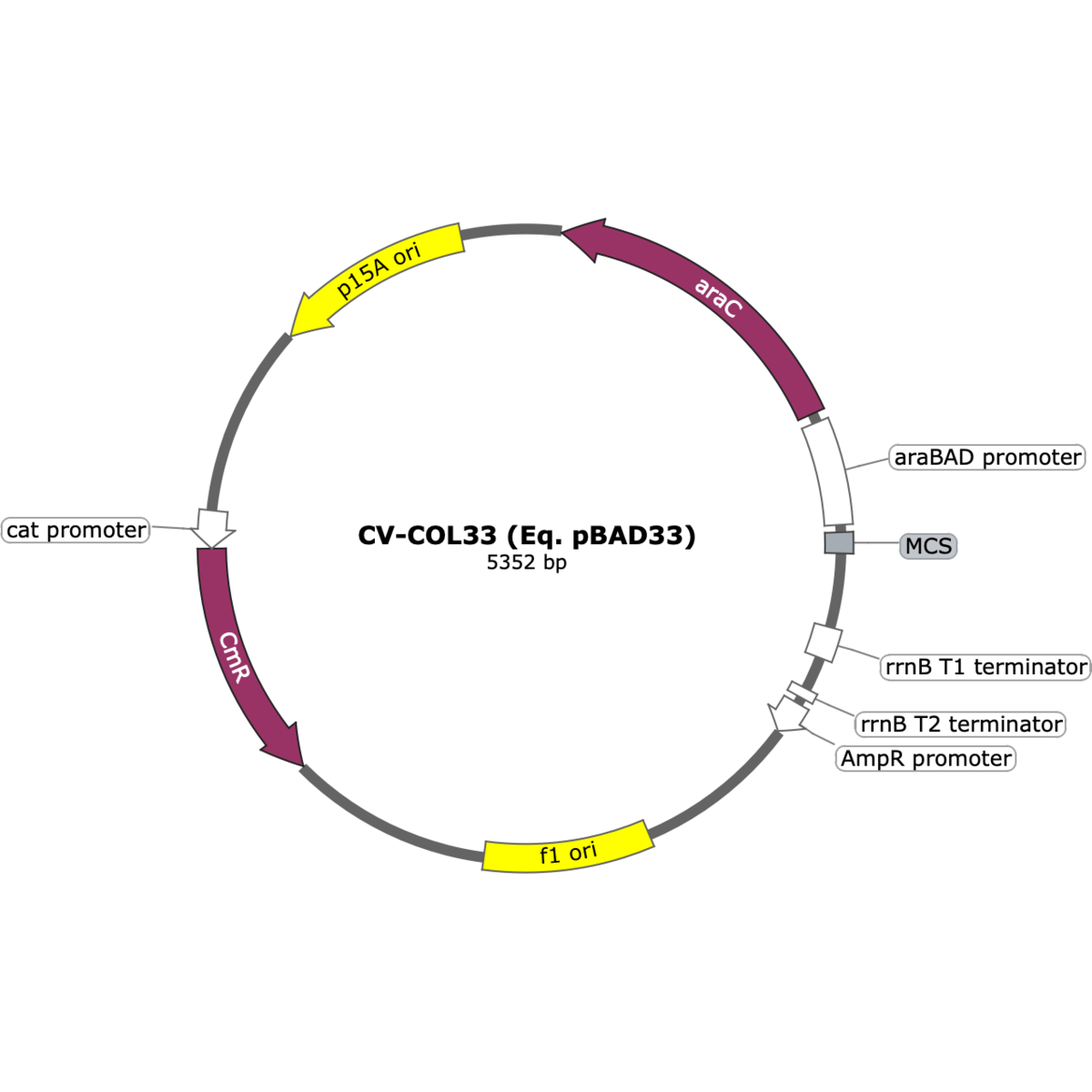
CV-COL33 has a sequence identical to the pBAD33 expression vector. This low-copy plasmid carries a chloramphenicol resistance marker and a p15A origin of replication, and features the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter under AraC regulation. Its reduced copy number makes it especially useful for the controlled expression of toxic or burdensome proteins in E. coli.
Format: 2 tubes with 5 µg in 5 µl of TE
Couldn't load pickup availability
Key Properties
Applications: Bacterial Expression
Copy number: Low copy number
Expression: Inducible
Host: E. coli
Selection markers: Chloramphenicol (E. coli)
Sequence: CV-COL33_Eq._pBAD33.gb
Share
Background
pBAD33 was developed as part of the pBAD expression system to provide a low-copy alternative for arabinose-inducible gene expression in E. coli. Like pBAD24, it employs the PBAD promoter under AraC regulation but carries a p15A origin of replication and chloramphenicol resistance marker. The lower copy number reduces metabolic burden and makes it suitable for expressing toxic or difficult proteins. CV-COL33 preserves the exact sequence of pBAD33, ensuring compatibility with established protocols. The original description can be found in: Guzman, L.M., Belin, D., Carson, M.J., & Beckwith, J. (1995). Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol., 177(14), 4121–4130.
Features
- Antibiotic selection: Chloramphenicol (cat)
- Origin of replication: p15A, low copy (~10–12/cell)
- Size: ~4.6 kb
- Promoter system: PBAD promoter, AraC-regulated, arabinose-inducible
- Regulatory elements: araC gene included on plasmid
- MCS: Multiple cloning site downstream of PBAD promoter
Applications
- Expression of toxic or unstable proteins
- Controlled metabolic engineering where reduced gene dosage is beneficial
- Experiments requiring both pBAD24 and pBAD33 for dual-plasmid systems with different copy numbers and markers
- Teaching inducible expression with alternative backbones
Limitations
- Lower DNA yields compared to ColE1-based vectors
- Requires arabinose for induction; expression is dose-dependent
- Lower maximal expression than T7-driven systems
- Limited to E. coli expression
