CV-COLCDF (Eq. pCDFDuet-1)
CV-COLCDF (Eq. pCDFDuet-1)
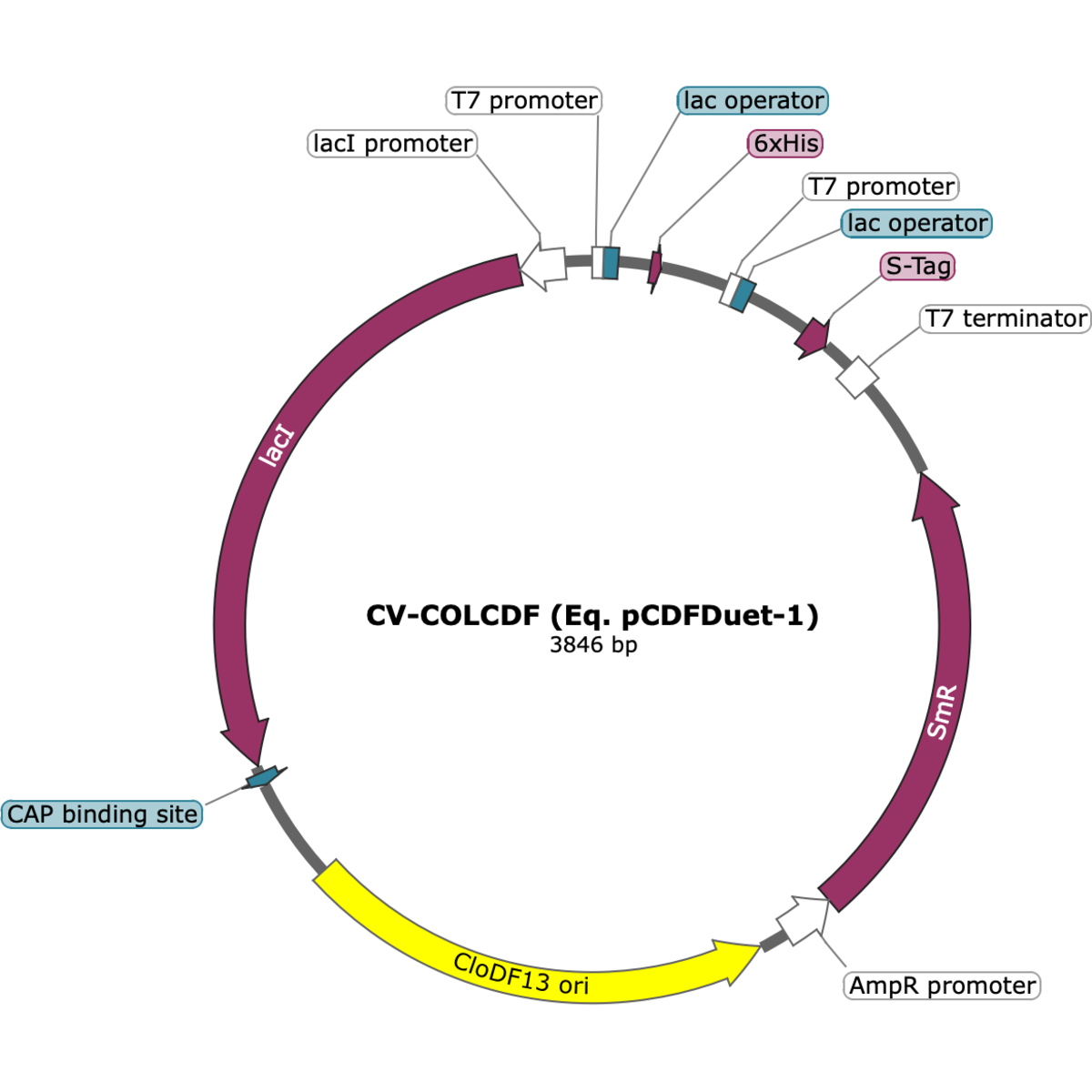
CV-COLCDF has a sequence identical to the pCDFDuet-1 co-expression vector. This plasmid carries a streptomycin/spectinomycin resistance marker and a CloDF13 origin of replication, ensuring stable maintenance at low copy number. It includes two T7 promoter-driven multiple cloning sites with ribosome binding sites, enabling coordinated expression of two target genes in E. coli.
Format: 2 tubes with 5 µg in 5 µl of TE
Couldn't load pickup availability
Key Properties
Applications: Bacterial Expression
Copy number: Low copy number
Expression: Constitutive
Host: E. coli
Selection markers: Streptomycin (E. coli)
Sequence: CV-COLCDF_Eq._pCDFDuet-1.gb
Share
Background
pCDFDuet-1 was introduced by Novagen as part of the Duet™ vector family, designed to enable co-expression of two target genes in E. coli. CV-COLCDF preserves the exact pCDFDuet-1 sequence, ensuring compatibility with published protocols and literature. The CloDF13 origin confers a low copy number, making this plasmid particularly useful for expressing proteins that may be toxic when overproduced. Original documentation is available in the Novagen manuals: pCDFDuet-1 Vector Manual (PDF) and Duet Vectors Protocol TB340 (PDF).
Features
- Antibiotic selection: Streptomycin/spectinomycin (aadA)
- Origin of replication: CloDF13 (low copy, ~5–10/cell)
- Size: ~4.3 kb
- Expression system: Two T7 promoters, each with a ribosome binding site and multiple cloning site
- Compatibility: Low-copy origin allows stable co-maintenance with ColE1- and p15A-derived vectors in the same cell.
Applications
- Co-expression of proteins that are toxic at high copy number
- Balanced multi-protein complex assembly
- Metabolic engineering where lower plasmid load improves host viability
- Protein–protein interaction assays
- Combination with other Duet vectors for multi-plasmid systems
Limitations
- Requires a host strain expressing T7 RNA polymerase (e.g., BL21(DE3))
- Lower plasmid yields compared to medium- or high-copy vectors
- No regulatory system beyond the T7 promoter; risk of basal expression
- Restricted to E. coli expression
