CV-COL24 (Eq. pBAD24)
CV-COL24 (Eq. pBAD24)
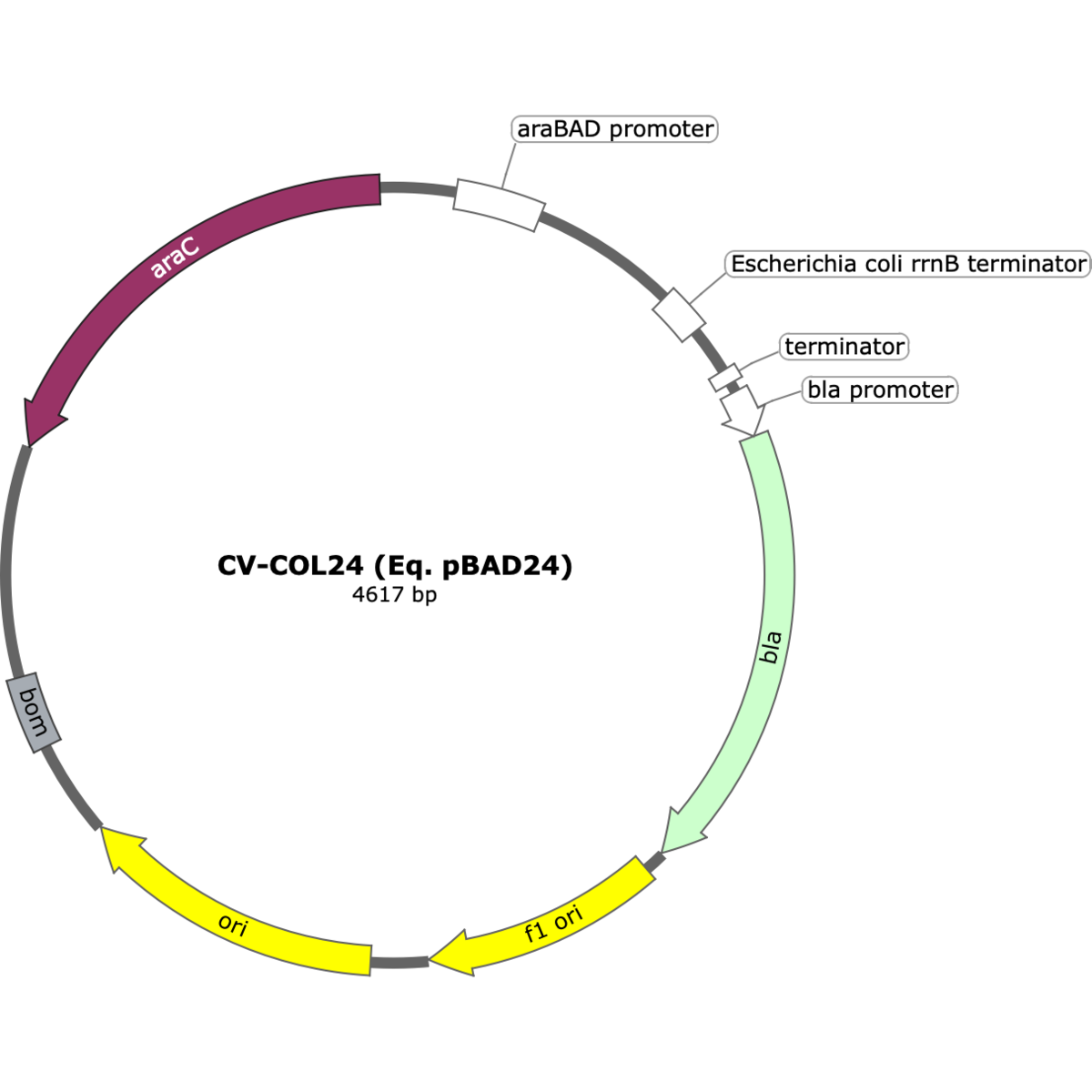
CV-COL24 has a sequence identical to the pBAD24 expression vector. This medium-copy plasmid carries an ampicillin resistance marker and a ColE1-derived origin, and features the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter regulated by AraC. It provides tight, tunable control of gene expression in E. coli, making it especially useful for cloning and expressing toxic or tightly regulated proteins.
Format: 2 tubes with 5 µg in 5 µl of TE
Couldn't load pickup availability
Key Properties
Applications: Bacterial Expression
Copy number: Medium copy number
Expression: Inducible
Host: E. coli
Selection markers: Amp / Carb (E. coli)
Sequence: CV-COL24_Eq._pBAD24.gb
Share
Background
pBAD24 was developed as part of the pBAD expression system, which employs the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter under control of the AraC regulator. This system provides tight, titratable regulation of gene expression in E. coli by varying arabinose concentration. CV-COL24 preserves the exact sequence of pBAD24, ensuring compatibility with published protocols. The original description can be found in: Guzman, L.M., Belin, D., Carson, M.J., & Beckwith, J. (1995). Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol., 177(14), 4121–4130.
Features
- Antibiotic selection: Ampicillin (bla)
- Origin of replication: ColE1-derived, medium copy (~15–20/cell)
- Size: ~4.5 kb
- Promoter system: PBAD promoter, AraC-regulated, arabinose-inducible
- Regulatory elements: araC gene included on plasmid
- MCS: Multiple cloning site downstream of PBAD promoter
Applications
- Expression of toxic or tightly regulated proteins
- Metabolic engineering where graded induction is advantageous
- Functional studies requiring fine control of gene dosage
- Teaching inducible expression systems in bacterial genetics courses
Limitations
- Requires arabinose for induction; expression strength depends on inducer concentration
- Lower maximal expression compared to T7-based systems
- Medium copy number yields less plasmid DNA than high-copy vectors
- Restricted to E. coli expression
